
What is Network Data?
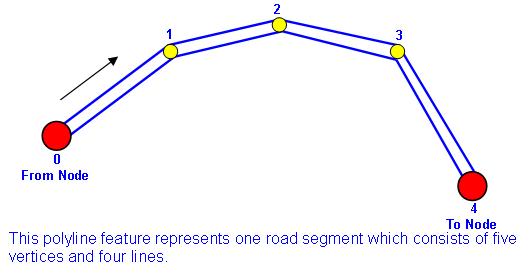
Map is the display of the result of overlapped layers. The layers can be classified into three types based on the characteristic; they are point, polyline and polygon layers. In route planning, the line layer which represents road is the necessary and basic layer. A line layer consists of many line features, and a line feature consists of vertices. Please see the figure below. The feature consists of five vertices, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and four lines. Among the vertices of the line feature, the beginning and the end vertices are called “Node”, which are 0 and 4 in the figure. It is decided by the digitizing direction of the feature. See the arrow in the figure, and we learn that 0 is the beginning Node, we call it “From Node.” 4 is the end Node, and we call it “To Node.” As a result, we know that the segment is made of two or more than two vertices, and several segments compose a road. Please note that the digitizing direction refers to the digitizing direction when a feature is beginning to edit instead of the road direction.
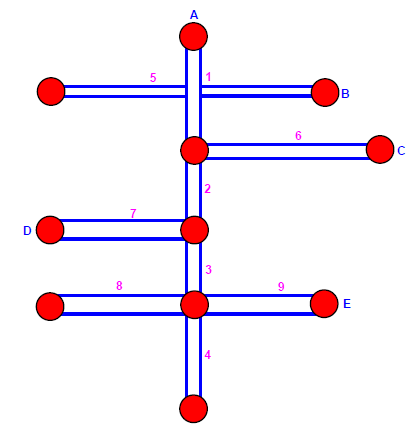
To the road layer, several segments compose a road or route. When a road connects another road, the cross point appears, and the segments are generated. Please see the figure below; in the figure, road A connects road C, D and E, it contains four segments: 1, 2, 3 and 4. To road E, it contains two segments: 8 and 9. Please note that if two roads intersect each other on the map, the cross point will be presented as a Node; however, two parallel roads do not intersect each other, for instance, a road and an overpass (or underground passage) do not connect each other but they cross over the air at different elevation. In such case, they will be presented with crossed line without node on the map. Please see the road A and B in the figure below; no node appears at the cross point, which means the relation of the two may be a road and an overpass and they are just parallel in the air without connection. So we learn that segment 5 of road B and segment 1 of road A simply intersect in the air without connecting.
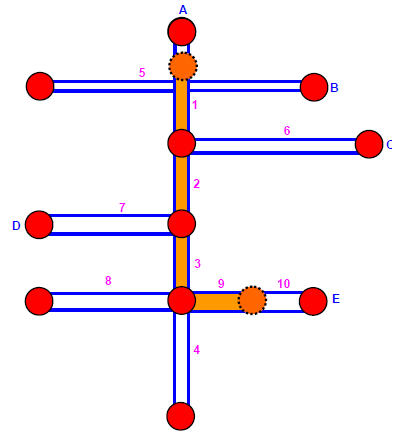
When the route planning is finished, a route result is obtained. A route result might contain one to several routes and a route is composed of several segments (the segments generated after solving will be called route segment). Segment and route segment is not exactly identical; the From node and the To node of the route segment might be the same as that of segment, but they might fall on part of the segment instead of covering the entire segment. So route segment might be equal to or smaller than the segment it belongs to.
Please see the figure below, segment 1, 2, 3 and 9 all belong to route segment. Among the route segments, the route segment 9 occupies around half of the original segment but route segment 3 covers the complete original segment.
Network data not only consists of geometric segments but also the attributes information such as cost, hierarchy, etc. The following sections will introduce the network element, network attributes and the SuperGIS Network file- NRT.
©2016 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.