
Create, Validation and Clean
Create Topology: Before creating topology and perform topology analysis, we need to add layers from Geodatabase Client, and create topology using Create Topology. Here we need to create a name for the new topology, set Cluster tolerance and select the layers to analyze as well as the output folder. Cluster tolerance is a value of length, if the distance between two vertices is smaller than Cluster tolerance, the system will automatically snap them (a typical example is the topology rule, “Must Be Larger than Cluster Tolerance”).
Validation:Validate the topology relationships based on the topology rules, target layers and aided layers and find out the areas and extent that violates the rules in an error list. In Topology Analyst 3, it has three types of validation:
1.Validate Topology in specified area: drag an area and validate the geometries within.
2.Validate Topology in current extent.
3.Validate entire topology, validate all the input layers.
As to the detailed topology rules, please refer to SuperGIS Topology Rules.
Clean finds all the intersections of line features and splits. By setting Cluster tolerance, the topology of line features will be created after some improper lines are fixed and cleaned such as zero length lines or snapping nodes and vertices that are too closed. After that, all the intersections of line features (including line feature intersects itself and line features intersect) will be found, and the duplicated segments (including partial overlapped line segment, entirely covered line segment, identical line segment) will be judged and removed based on the Cluster tolerance. The Cluster tolerance must not be 0; else some intersection might not be able to be found. At last, the dangle lines generated in digitization will be deleted based on Cluster tolerance.
Next, we will introduce the processes in performing Clean.
1. Remove the zero length line.

2. Find the intersections of lines that cross at one point (including a line feature intersects itself), in the mean time, delete the duplicated line segments.
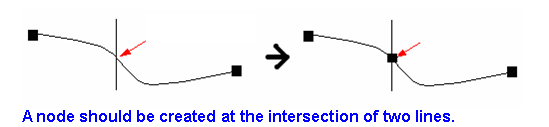
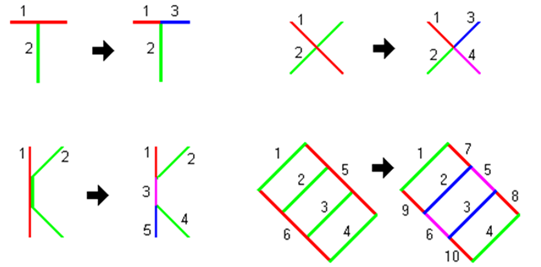
The intersection of the lines becomes a new vertex, and split the intersected lines to independent line features. In a plane two lines that intersect each other at a point should generate a vertex at the intersection point so that the connection status of the two can be presented. “Find intersection” is simply a term, in fact, there are some judgment rules and behaviors to implement. In processing, any two line segments may have the relationships as below:
(1) Line segment A does not intersect line segment B.
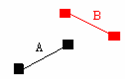
(2) Line segment A is exactly identical to line segment B.
![]()
(3) Line segment A contains the entire line segment B or line segment B contains the entire line segment A.
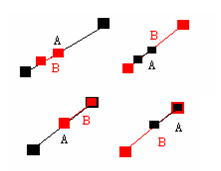
(4) Line segment A contains part of line segment B or line segment B contains part of line segment A.
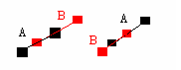
(5) One node of line segment A is one node of line segment B but the two line segments do not overlap.
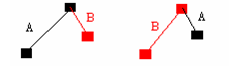
(6) One node of line segment A falls on line segment B or one node of line segment B falls on line segment A.
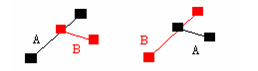
(7) Line segment A intersects line segment B at a point (not at the node of either line segment).
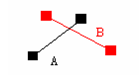
We need to consider the relationships mentioned above when finding the intersections. In the process, the duplicated line segments will be removed based on Cluster tolerance. The figure below is the comparison of before processing and after processing.
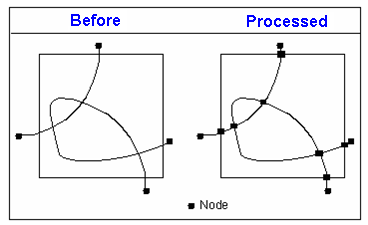
3. Remove the nodes that are duplicated or too close (the distance of nodes is smaller than Cluster tolerance).
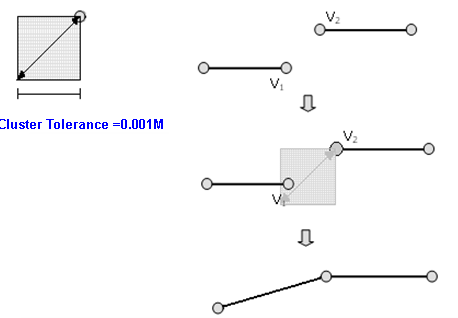
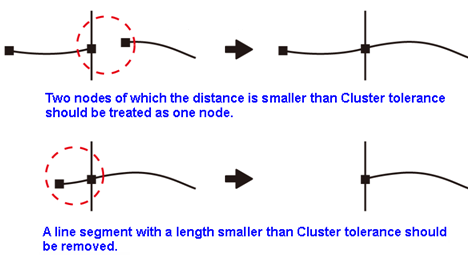
Before, in or after the process of finding intersection, the distance of any two nodes or turn points is shorter than Cluster tolerance should be treated as one node. Therefore, we need to remove the nodes which are duplicated or too close. Please see the figure below the comparison of before and processed.

The Clean is finished. Now any two line segments that intersect should intersect at node only; the distance between any two coordinates should be greater than Cluster tolerance, and the short line segment that is shorter than Cluster tolerance does not exist.
©2014 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.