
Variography
Assuming that Z(x) is a regionalized random variable and satisfies Second-Order Stationary and Intrinsic Hypothesis, h is the spatial distance between any two samples, Z(xi) and Z(xi+h) are the observed values of the regionalized variable Z(x) at the spatial location xi and xi+h (i=1,2,…., N(h)), respectively, the equation is:
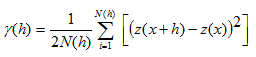
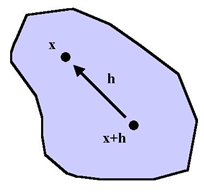
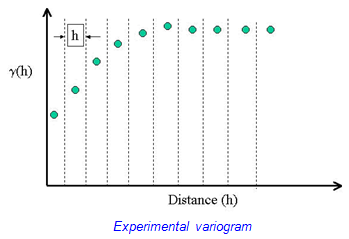
Where h is the x-axis, and y(h) is the y-axis,. When we draw a variable function curve to present the spatial variability of the regionalized variable Z(x), this is called experimental variogram. This is also an effective tool for spatial analysis and structure analysis.
©2017 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.