Slope
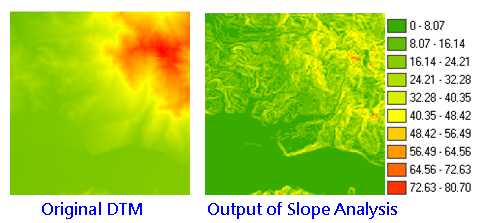
Slope analysis calculates the change rate in value for a cell to its neighbors; that is, the steepness or flatness on the surface. On the output layer, each cell has a slope value, the smaller value stands for the flatter terrain; the larger value stands for the steeper terrain.
In Output Measurement, SuperGIS Spatial Analyst 3 provides three different measurement, percentage, degree and radius.
1.![]() Percentage
Percentage
The most common method, it calculates each cell and the neighboring cell with DTM and get the percentage of elevation difference and horizontal distance. The formula is: Slope =(elevation difference/horizontal distance*100%) Example: Slope of 3 % stands for that whenever the horizontal distance is offset by 100 meters, the vertical distance goes up(or goes down) by three meters. Slope of 15% stands for whenever the horizontal distance is offset by 100 meters, the vertical distance goes up(or goes down) by 15 meters and so on. |
2.![]() Degree
Degree
Represents the slope by degree. The degree is obtained by inverse Trigonometric functions, the formula is: Slope angle= If slope angle( If slope angle( If slope angle( So the steeper slope has larger tan. |
3.![]() Radius
Radius
The perimeter of circle =2 The angle multiplies the circular ratio(3.1415926...) and divided by 180. So, the perimeter of circle is 2
|
With Slope analyst, we can get:
1.The dense level of contour(the denser contours represents the steeper slope).
2.The shape of the contour(convex slope: the contour is much denser at lower elevation, and gradually sparse to higher elevation; concave slope: the contour is much denser at higher elevation and gradually sparse to lower elevation. )
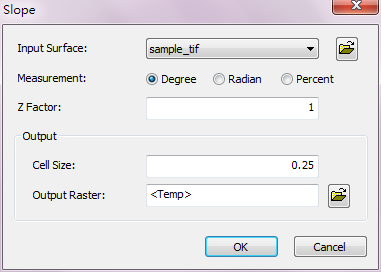
Description of Parameters
Item |
Description |
Data Type |
Input Surface |
The data to perform slope analysis. |
Raster layer |
Measurement |
Switch measurement type: •Degree •Radian •Percent |
Measurement options. |
Z Factor |
The default is 1; it means the unit of vertical and horizontal direction are the same. |
Integer/floating point |
Cell Size |
The cell size of the output raster. |
Integer/floating point |
Output Raster |
The filename and storage path of the output raster. |
Raster layer |
©2016 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.