
Resample Analysis
Resample Analysis adjusts the output cell data in the same extent by changing cell size or resampling. The system provides four commonly used re-sampling methods;
1.Nearest Neighbor: Suitable for data more dispersed. It generates new values by interpolating the four neighbor cell values. It does not change the values of original cells. The maximum spatial inaccuracy is half the standard cell size, which is the quickest and simplest interpolation.
2.Bilinear Interpolation: Suitable for successive data. It produces the smoother result than Nearest Neighbor because it performs linear interpolation twice to the four neighbor cell values. So, the result has the misty visual effect and the edge part has worse effect.
3.Cubic Convolution:Suitable for successive data. It performs cubic convolution vertically to the nearest 16 neighbor cells for four times and perform horizontally one time to the obtained result. The operation of this algorithm takes the longest time, and the output cell data could be cell value other than the input raster.
4.Majority: Calculates the input raster with the filter window. Similar to the Nearest Neighbor, it is mainly used to calculate the dispersed data. The output raster is smoother than that of Nearest Neighbor.
Description of Parameters
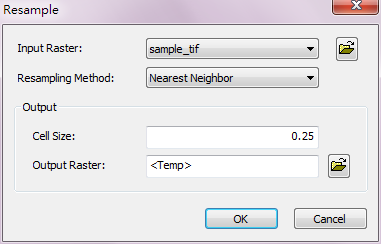
Item |
Description |
Data Type |
Input Raster |
The data raster that will resample. |
Raster layer |
Resampling Method |
The method to resample. |
Feature layer |
Cell Size |
The cell size of the output raster. |
Integer/Floating point |
Output Raster |
The filename and path of the output raster. |
Raster layer |
©2016 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.