
Spatial Join
"Spatial Join" is a type of spatial analysis, applying the spatial relationship between layers to join the two layers' attribute data to create a new layer. Therefore, the new layer still contains the features of the original layer, but the attribute data of the new layer will add new fields or be appended with the fields of the other layer. For example, when you would like to find out how many gas stations in a certain district or search the nearest restaurants, you can apply "Spatial Join" to fulfill the goal. So, you can open "Spatial Join" window, choose the target layer and the joined layer, and specify the operation. Then, the layers can be joined to create a new layer and a new attribute table. The way to open "Spatial Join" window is to click "Tools" menu and click "Spatial Join" on the menu.
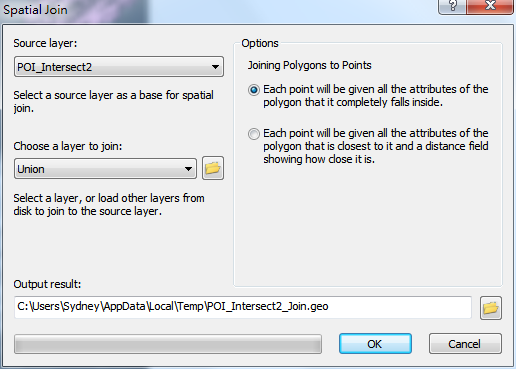
In "Spatial Join" window, there are "Source Layer" drop-down menu and "Choose a Layer to Join" drop-down menu. The menus list all of the layers displaying in the current project. You can choose the layer for "Source Layer" as the spatial join base and choose the layer you would like to join for "Choose a Layer to Join." If the layer you would like to join is not in the current project, you can click .png) to browse the layer you need. According to the layer type you choose in the menu, the right side of the window shows different operations. You can choose the most suitable operation to join the layers to meet your needs. Then, you can confirm the path for saving the output layer; the default folder is the folder of the source layer. As all the settings are finished, click "OK." Then, the progress bar at the bottom of the window shows the progress of the operation. There are different operations for joining different types of layers. The join operations for each type of layer are introduced in the following table.
to browse the layer you need. According to the layer type you choose in the menu, the right side of the window shows different operations. You can choose the most suitable operation to join the layers to meet your needs. Then, you can confirm the path for saving the output layer; the default folder is the folder of the source layer. As all the settings are finished, click "OK." Then, the progress bar at the bottom of the window shows the progress of the operation. There are different operations for joining different types of layers. The join operations for each type of layer are introduced in the following table.

|
Point layer
|
Polyline layer
|
Polygon layer
|
Point layer
|
•
|
Each point will be given a count field showing how many points are closest to it, and a summary of the numeric attributes of the points.
|
•
|
Each point will be given all the attributes of the point that is closest to it and distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
•
|
Each line will be given a count field showing how many points are intersected by it, and a summary of the numeric attributes of the points.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the point that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given a count field showing how many points fall inside it, and a summary of numeric attributes of the points.
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given all the attributes of the point that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
Polyline layer
|
•
|
Each point will be given a count field showing how many lines intersect it, and a summary of the numeric attribute of the lines.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the line that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
•
|
Each line will be given a count field showing how many lines intersect it, and a summary of the numeric attribute of the lines.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the line that is part of.
|
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given a count field showing how many lines intersect it, and a summary of the numeric attribute of the lines.
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given all the attributes of the line that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
Polygon layer
|
•
|
Each point will be given all the attributes of the polygon that it completely falls inside.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the polygon that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
•
|
Each line will be given a count field showing how many polygons it intersects, and a summary of the numeric attribute of the polygons.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the polygon that it completely falls inside.
|
•
|
Each line will be given all the attributes of the polygon that is closest to it and a distance field showing how close it is.
|
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given a count field showing how many polygons intersect it, and a summary of the numeric attribute of the polygons.
|
•
|
Each polygon will be given all the attributes of the polygon that it completely falls inside of.
|
|
©2015 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.

![]() to browse the layer you need. According to the layer type you choose in the menu, the right side of the window shows different operations. You can choose the most suitable operation to join the layers to meet your needs. Then, you can confirm the path for saving the output layer; the default folder is the folder of the source layer. As all the settings are finished, click "OK." Then, the progress bar at the bottom of the window shows the progress of the operation. There are different operations for joining different types of layers. The join operations for each type of layer are introduced in the following table.
to browse the layer you need. According to the layer type you choose in the menu, the right side of the window shows different operations. You can choose the most suitable operation to join the layers to meet your needs. Then, you can confirm the path for saving the output layer; the default folder is the folder of the source layer. As all the settings are finished, click "OK." Then, the progress bar at the bottom of the window shows the progress of the operation. There are different operations for joining different types of layers. The join operations for each type of layer are introduced in the following table.
