Slope
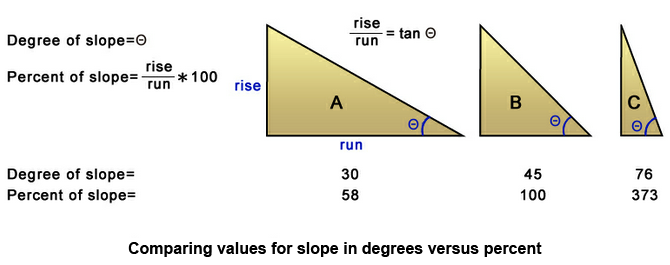
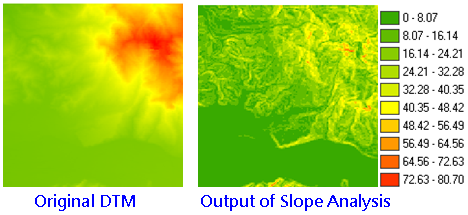
Slope analysis calculates the change rate in value for a cell to its neighbors; that is, the steepness or flatness on the surface. On the output layer, each cell has a slope value, the smaller value stands for the flatter terrain; the larger value stands for the steeper terrain. In Output Measurement, SuperGIS 3D Analyst 10 provides three different measurement, percentage, degree and radius.
1. Percentage The most common method, it calculates each cell and the neighboring cell with DTM and get the percentage of elevation difference and horizontal distance.The formula is: Slope = (elevation difference/horizontal distance*100%) Example: Slope of 3 % stands for that whenever the horizontal distance is offset by 100 meters, the vertical distance goes up (or goes down) by three meters. Slope of 15% stands for whenever the horizontal distance is offset by 100 meters, the vertical distance goes up (or goes down) by 15 meters and so on.
2. Degree Represent the slope by degree. The degree is obtained by inverse Trigonometric functions, the formula is: Slope angle=Θ, tanΘ=b/a. If slope angle (Θ) is 45 degrees, it means the a=b, tanΘ=1. If slope angle (Θ) is 30 degrees, tan 30= If slope angle (Θ) is 60 degrees, tan 60= So the steeper slope has larger tan.
3. Radius The perimeter of circle =2 The angle multiplies the circular ratio (3.1215926...) and divided by 180. So, the perimeter of circle is 2
With Slope analyst, we can get: 1.The dense level of contour (the denser contours represents the steeper slope). 2.The shape of the contour (convex slope: the contour is much denser at lower elevation, and gradually sparse to higher elevation; concave slope: the contour is much denser at higher elevation and gradually sparse to lower elevation.)
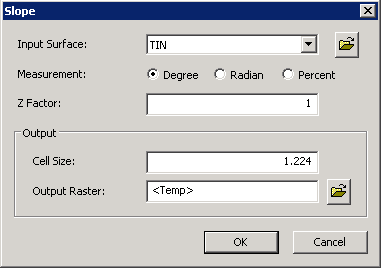
Description of Parameters
©2016 Supergeo Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. |